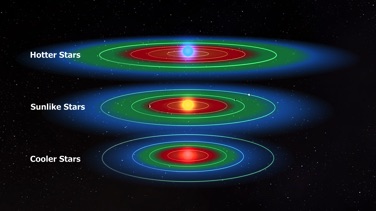
The location of the habitable zone surrounding a star is determined by the luminosity of that particular star. Hotter stars can deliver more energy over time to the surface of an individual exoplanet than can cooler stars. An exoplanet is in the habitable zone of a star if the exoplanet’s surface receives enough energy over time so that its surface temperature could support the existence of liquid water.
Earth 2?
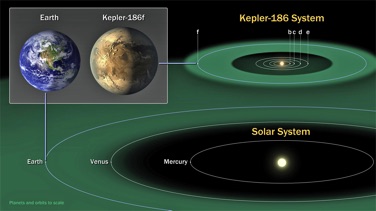
In April 2014 NASA announced the discovery of Kepler-186 f. This exoplanet was discovered from data compiled by the Kepler spacecraft. Kepler-186 f is unique because it is the first confirmed Earth-sized exoplanet to be discovered within the habitable zone of its central star. Kepler-186, the central star, is half the size and mass of the Sun. Kepler-186 has a solar system that contains 5 known exoplanets, the most prominent of which is Kepler-186 f.